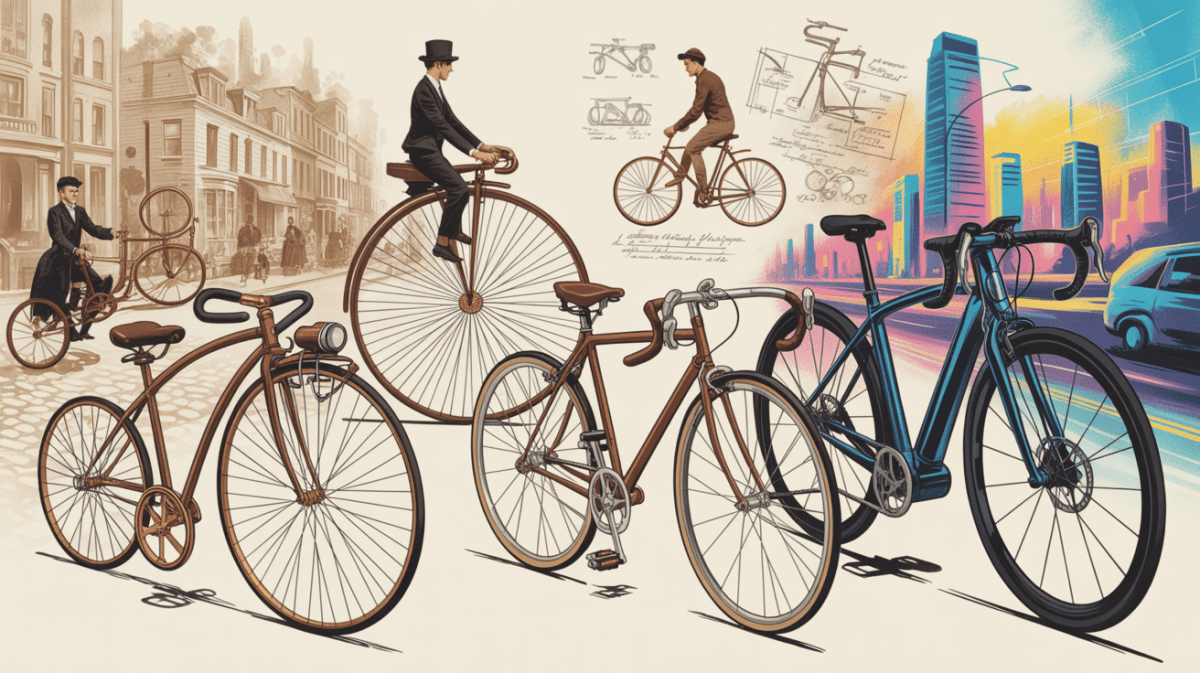The history of the bicycle is an ongoing journey that began more than two centuries ago. Early riders of these two-wheeled vehicles were often derided as dangerous and reckless. Still, since the 19th century, the bicycle has become a symbol of freedom and exploration the world over. Throughout time, cycling has inspired incredible innovation, pushed the envelope of human strength and endurance and contributed to advancements in science and technology.
The invention of the modern bicycle dates as far back as 1817, when German Baron Karl von Drais invented a two-wheeled, steerable machine that he called the Laufmaschine, or “running machine.” This invention was the first step in what would eventually become the lightweight and efficient modern bicycle that we know today. The introduction of the rotary crankset in the late 1850s was a pivotal step in the evolution of the bicycle – allowing riders to use their feet to propel the machine rather than simply running it along with their own feet. The crankset also enabled the development of a chain-driven bicycle, which debuted in the 1860s.
The introduction of the pneumatic tire revolutionized cycling, enabling riders to travel farther and faster with significantly less effort than ever before. The pneumatic tire was invented in 1888 by Scotsman John Boyd Dunlop, and within a few short years, the invention had been put to use on dozens of different bicycle models. Following the invention of the pneumatic tire, bicycle manufacturers began experimenting with various materials and designs to enhance the rider experience.
Today, the bicycle remains a lasting symbol of adventure, exploration, and freedom. Whether used for leisure, sport, or practical transportation, the bicycle is a multifaceted vehicle that continues to have a positive impact on our daily lives. From racing bikes to everyday commuter bikes, the bicycle continues to evolve and change with each passing year.
Invention of the Bicycle
The invention of the bicycle is credited to several inventors in the early 19th century. The earliest known mechanical bicycle-like structure was developed in 1817 by Baron von Drais, a German civil servant. It's design called for two same-size in-line wheels connected by a frame on which the rider sat. The rider propelled the machine by pushing it along with his feet. The Drais machine had no pedals, so it was really more of an early precurser to the skateboard rather than the bicycles we know today.
Despite its limitations,Interest in the Drais machine spread in Europe and North America. The British inventor Denis Johnson made several improvements to the design, including the addition of pedals and a steering linkage. The next major development came in 1839 with the invention of the "Velocipede" by a Scotsman named Kirkpatrick MacMillan. MacMillan's version used two same-size wheels, but it had a slightly different frame and added pedals.
The most popular early bicycle designs differed significantly from traditional bicycles. Several variations of the velocipede were mass-produced throughout Europe. These so-called penny-farthing bikes featured a large front wheel and a small rear wheel, connected by a single-speed gear. The rider sat very high on the bike, and scooted forward with a pushing motion on the pedals. Although uncomfortable to ride, these penny-farthings became quite popular.
In the late 19th century, the "safety bicycle" was developed. This was the first version of the modern bicycle, featuring two wheels of the same size and a pedal-driven transmission. These bicycles were much more comfortable to ride and far easier to maneuver than their predecessors. In the 1860s, the safety bicycle was further refined and mass-produced. By the end of the 19th century, the modern bicycle was widely available around the world.
Popularity and Uses of Bicycles
Since their invention, bicycles have become one of the most popular forms of transportation and recreation worldwide. Although the shape, size, and materials they are made from have evolved, bicycles continue to provide efficient, healthy, and eco-friendly transportation.
Bicycles are used for a variety of purposes, including commuting, racing, touring, exercise, and even transporting goods or materials. The most popular types of bikes are road bikes, designed for short to medium-distance rides on paved surfaces, and hybrid bikes, which combine features of a mountain bike and a road bike.
In the United States, bicycle commuting is becoming increasingly popular; in 2015, more than 860,000 Americans commuted by bicycle. An additional 47 million people also ride bicycles for recreation and exercise. With the ever-increasing recognition of the environmental and health benefits of cycling, more people are riding bicycles as an alternative form of transportation.
Development of Bicycle Technology
Since the invention of bicycles many years ago, technology has advanced rapidly to make modern-day bicycles safer, faster, and more efficient than ever before. Different materials such as carbon fibre and aluminium are used to construct a lighter but stronger frame, and tyres, gears, chains and brakes are all built to much higher quality and safety standards. The geometry of the frame has also been constantly improved, making it more comfortable and efficient to ride. Technology such as shock-proof suspension systems makes even rough terrain much easier to handle.
In the 1990s, similar to the car industry, electric bicycles began to appear in the market. Pedal power was still mixed with a battery powered motor, providing an easier and less strenuous way of riding a bicycle. Jump forward another ten years, and electric bicycles and various other forms of power-assisted bicycles became increasingly popular, with sales high and new innovative designs appearing all the time.
Today, there are also bicycles designed for racing, such as mountain bikes, track bikes and cruisers. These are built with much sturdier and lighter materials, such as carbon fibre and titanium, and feature specialised components like disc brakes and customised gears to enhance overall performance. Racing bicycles are also engineered to be aerodynamic, specially designed with riders in mind so that they can race faster with less effort.
Impact of Bicycles on Society
The invention of the bicycle has had a tremendous impact on society since its appearance in the 19th century. One of the more notable impacts is the environmental benefit of reducing traffic pollution.
Bicycles require much less energy than motorized transportation, making them the most energy-efficient form of transport available for short distances. Bikes can generally reduce commuter times and also help alleviate congestion on popular roads and paths. The introduction of bicycle lanes, bike-sharing, and other bike-friendly infrastructure has encouraged more people to ride bikes as part of their day-to-day activities.
Another major way in which bicycles have impacted society is in terms of economic and social mobility. In the early days of the bicycle, its affordability and lightness, compared to horse-drawn carriages, meant that many people who would not have been able to afford the luxury of horse-drawn transportation were now able to move around, making it possible to find new job opportunities while offering leisure time away from home.
The impact of bicycles on society has been felt in health and fitness too. The addition of bicycle-friendly infrastructure has helped to encourage people of all ages and gender to cycle, making it an activity that is accessible to everyone regardless of the availability of money or to buy a motorized vehicle.
The contributions of bicycles to society are vast and varied, ranging from environmental benefits to economic mobility, from health advantages to leisure. As we move forward, we must continue to develop the infrastructure and policies necessary to integrate bicycles into our lives and contribute to a more sustainable, healthier future.
Present and Future of Bicycles
Bicycling has continued to evolve over the years and is popular among both leisure cyclists and those seeking it as a form of exercise. Over the past few decades, there has been a shift away from traditional bicycle designs, as cyclists seek more efficient and comfortable options. The introduction of electric bicycles has made cycling more accessible to a wider range of people, allowing cyclists to commute over greater distances without becoming as tired.
The future of bicycling appears to be a continuation of these trends, with an increasing number of people seeking innovative and comfortable ways to ride. The development of connected technology and smart bikes appears poised to revolutionize the cycling experience, making life easier for urban riders. Autonomous bikes are also in development, enabling cyclists to experience the freedom of riding without worrying about having too little energy to complete the journey.
In the future, it is likely that more and more people will turn to bicycling as a way to get around and stay active. As the designs and technology continue to improve, more people, both young and old, are sure to find value in this form of transportation.
DISCLAIMER
This document is provided for general information purposes only and should not be relied upon as providing legal advice, technical, or specific operational guidance to the reader, whether as to the practices described in the document or the applicable legal requirements and regulations. Just Electric Bikes expressly disclaims any responsibility for liability arising from or related to the use or misuse of any information in this document.